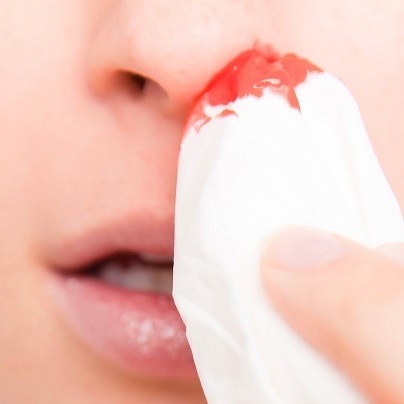

How To Stop Nosebleeds By ENT Specialists in Hyderabad
https://www.lybrate.com/hyderabad/ear-nose-throat-ent-specialist
Find out the methods that can help one at the time of nosebleeds
About this Accelerator
Nosebleeds or nose bleeding is a very common thing and the medical name for a nosebleed is epistaxis. ENT Specialists in Hyderabad says that It seems scary but they don’t indicate any serious medical problem. The nose contains many blood vessels, which are located close to the surface in the front and back of the nose. They’re very fragile and bleed easily. Nosebleeds are common in both adults and children.
Different Kinds Of Nosebleeds
1. Anterior Nosebleed:
The most common kind of nosebleed is an anterior nosebleed, which comes from the front of the nose. Very small blood vessels, that are inside the nose may break and bleed, causing this type of nosebleed.
2. Posterior Nosebleed:
Another kind of nosebleed is a posterior nosebleed, which comes from the deepest part of the nose. The blood from a posterior nosebleed flows down the back of the throat even if the person is sitting or standing. Youngsters rarely have posterior nosebleeds, it occurs most often in older people, people who have high blood pressure, and people who have had nose or face injuries.
What Causes Nosebleed
There are many causes of nosebleeds. A sudden or infrequent nosebleed is rarely serious. If you have frequent nosebleeds, you could have a more serious problem.
The most common cause of anterior nosebleeds is dry air. A dry climate or heated indoor air dries out nasal membranes, causing crusts that may itch and then bleed when scratched or picked.
Other, less common can be taking antihistamines and decongestants for allergies, colds, or sinus problems can also dry out the nasal membranes and cause nosebleeds. Frequent nose blowing is another cause of nosebleeds. A rare cause of frequent nosebleeds is a disorder called hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia (HHT). Sometimes, the cause of nosebleeds can’t be determined.
Other common causes of nosebleeds include:
- chemical irritants
- allergic reaction
- injury to the nose
- repeated sneezing
- picking the nose
- cold air
- upper respiratory infection
- large doses of aspirin
Posterior nosebleed causes
- high blood pressure
- nasal surgery
- calcium deficiency
- exposure to chemicals that may irritate the mucous membrane
- blood diseases, such as hemophilia or leukemia
Preventing Nosebleeds
- Whenever you blow your nose (especially when you have a cold), you should blow gently into soft tissue. Don't blow forcefully or pick your nose.
- Your doctor may recommend a humidifier to moisten your indoor air. You can also prevent your nasal passages from becoming too dry in winter months by using lubricants such as an antibiotic ointment before going to bed at night.
- Apply a pea-sized dab to a cotton swab and gently rub just the cotton tip up inside each nostril, especially on the middle part of the nose (called the nasal septum). Some doctors prescribe saline (salt water) drops or gel for the same purpose.
- Wear protective athletic equipment when participating in sports that could cause injury to the nose.
Nose Bleeding First Aid
What to do to stop a nosebleed:
1. Firstly, sit down and firmly pinch the soft part of your nose, just above your nostrils, for at least 10-15 minutes
2. Then, lean forward and breathe through your mouth – this will drain blood into your nose instead of down the back of your throat
3. After that, place an ice pack or bag of frozen vegetables covered by a towel on the bridge of your nose
4. stay upright, rather than lying down, as this reduces the blood pressure in the blood vessels of your nose and will discourage further bleeding
5. If the bleeding continues after 10 to 15 minutes, repeat holding pressure for another 10 to 15 minutes. Avoid peeking at your nose. If the bleeding still continues, seek emergency care.
6. To prevent re-bleeding, don't pick or blow your nose and don't bend down for several hours after the bleeding episode. During this time, remember to keep your head higher than the level of your heart. You can also gently apply some petroleum jelly to the inside of your nose using a cotton swab or your finger.
7. If re-bleeding occurs, blow out forcefully to clear your nose of blood clots. Then spray both sides of your nose with a decongestant nasal spray containing oxymetazoline (Afrin). Pinch your nose again as described above and call your doctor.
When to seek emergency care
- The bleeding lasts for more than 30 minutes
- You feel faint or lightheaded
- The nosebleed follows an accident, a fall or an injury to your head, including a punch in the face that may have broken your nose
Locations
- Delhi, India
Industries
Healthcare Services , - show less